The share of federal spending devoted to children’s programs is projected to fall from 9.2 percent to 7.5 percent over the next decade, according to the latest analysis by the Urban Institute, as programs supporting senior citizens and interest payments on the national debt eat up more and more of the budget.
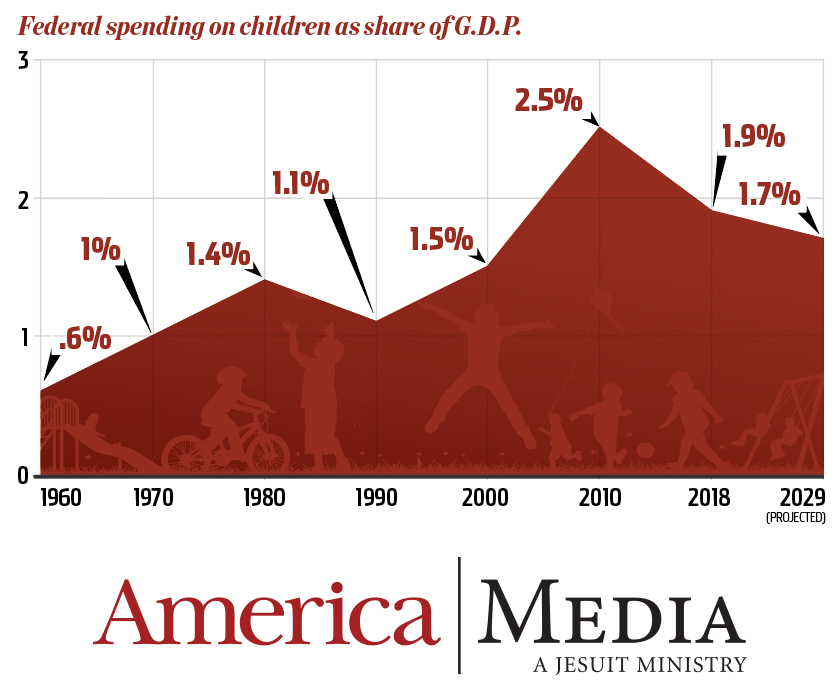
The 2019 “Kids’ Share” report, released in September, finds that federal spending on children fell to 1.9 percent of the U.S. gross domestic product in 2018, the lowest level in a decade.
Cuts in federal spending on education and nutrition programs, as well as a temporary reduction in child-related tax credits, accounted for the decline.
Even at 7.5 percent, the slice of the federal pie given to children’s programs would be more than double what it was in 1960 (3.3 percent).
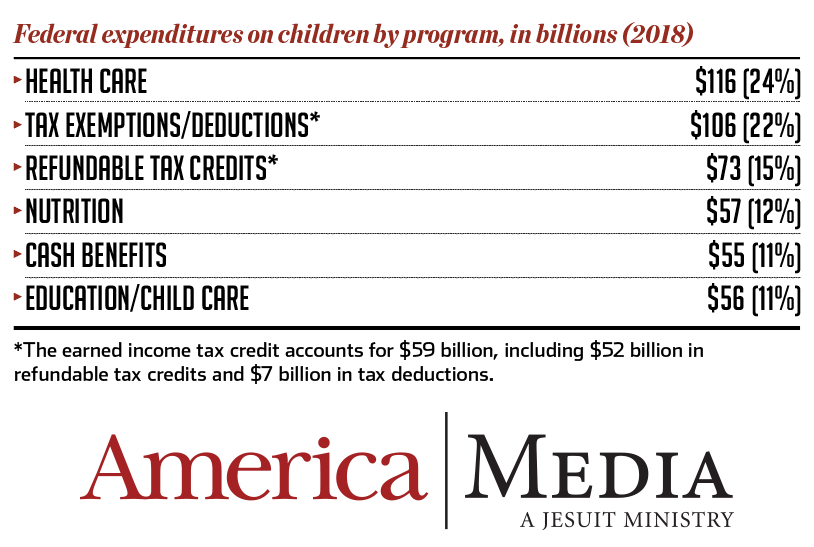
In that year, federal aid to children mostly took the form of cash payments and tax credits (in particular, the exemption for dependents), but that was before the introduction of many programs targeting health care, education and nutrition needs—and before a drastic reduction in defense spending from its Cold War highs.
It should be noted that most government spending on behalf of children is at the state and local levels, where public education is administered.
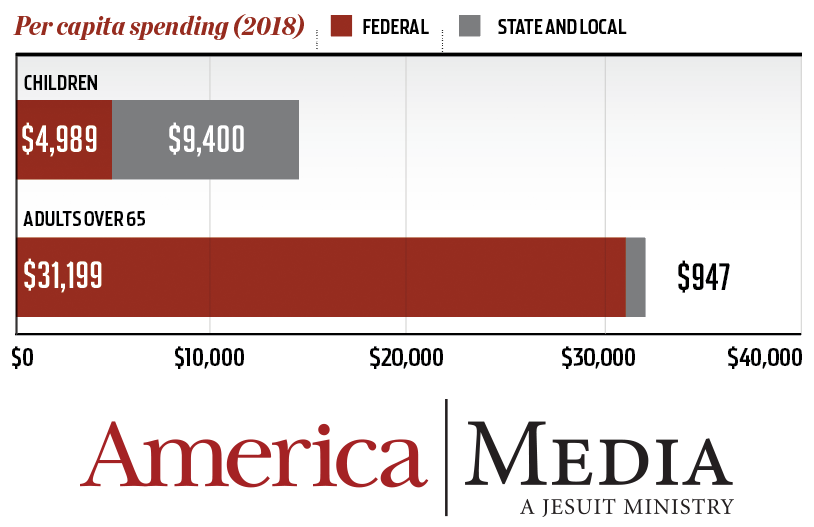
But combining all levels of government, the United States still spent more than twice the amount per capita to benefit older adults as it did for children in 2016—$32,146 per adult over the age of 65 versus $14,389 per child.
Looking forward from current trends, the Urban Institute projects that children’s programs will receive only 3 percent of a $1.5 trillion increase in federal spending over the next decade. (Defense spending is projected to remain at its current level, adjusted for inflation.)
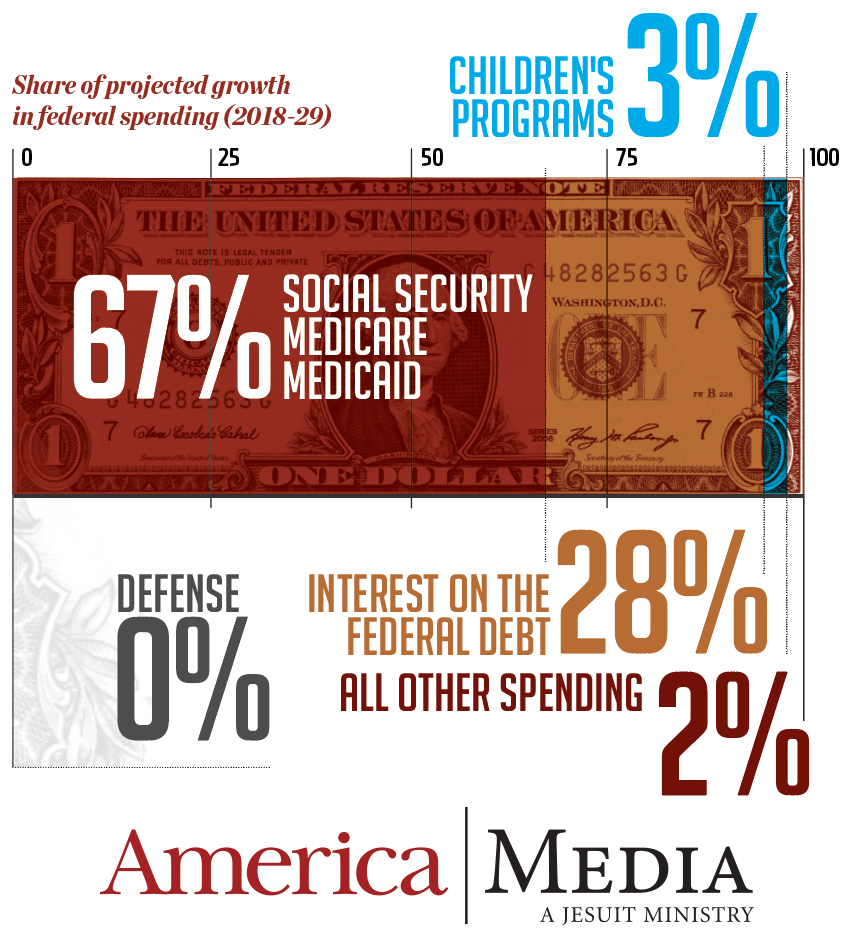
That means a bigger burden on state and local governments, assuming they do not want their children to fall behind in education and well-being. Some 60 years after Washington began an ambitious effort to iron out inequities, the level of government assistance available to a child may increasingly depend on where that child lives.
Source: Kids’ Share 2019: Report on Federal Expenditures on Children through 2018 and Future Projections, Urban Institute, Sept. 17, 2019.








